Application in Practice
This section includes a detailed explanation of how the DEMI model works, what a key control is and why it is important to define key controls in the risk-control matrix.
The DEMI model used at Vienna University of Technology is a flow chart that is characterised by clearly defined and concise responsibilities for each process step. For each process step, only one structural element or leader can be defined for "implementation" or "decision", while for cooperation and information, several structural elements or leaders can be listed.
- D ... Implementation (1 person responsible)
- E ... Decision (1 person responsible)
- M ... Collaboration (several structural elements possible)
- I ... Information (several structural elements possible)

Shown are the columns of the DEMI model from left to right: Input, Sequence, Output, D, E, M, I
Das an der TU Wien verwendete DEMI Modell, ist ein Flussdiagramm, das sich besonders durch die klar definierten und übersichtlichen Verantwortlichkeiten je Prozessschritt auszeichnet. Für jeden Prozessschritt kann immer nur ein Strukturelement oder ein_e Leiter_in für "Durchführung" oder "Entscheidung" definiert werden, während bei Mitarbeit und Information auch mehrere Strukturelemente beziehungsweise Leiter_innen angeführt werden können.
- D … Durchführung (1 Verantwortliche_r)
- E … Entscheidung (1 Verantwortliche_r)
- M … Mitarbeit (mehrere Strukturelemente möglich)
- I … Information (mehrere Strukturelemente möglich)
Die "Praxis Schulung IKS" erklärt die Anwendung des DEMI Modells im Detail.
- A key control is a financially risky control step whose risk is identified, assessed and assigned a specific control by the process manager.
- The task of a key control is to minimise or prevent the occurrence of risks through certain control activities.
- The risk assessment and the traceability of the execution of the key control is precisely documented in the risk-control matrix.
- The risk assessment is carried out through a realistic estimation of the amount of damage and the probability of occurrence.
Unter einer Key Control ist ein finanzrisikobehafteter Kontrollschritt zu verstehen, dessen Risiko vom_von der Prozessverantwortlichen erkannt, bewertet und mit einer bestimmten Kontrolle versehen wird.
- Dieser Kontrollschritt = Key Control hat als Aufgabe durch bestimmte Kontrolltätigkeiten den Risikoeintritt zu minimieren bzw. zu verhindern.
- Die Risikobewertung und die Nachvollziehbarkeit der Durchführung der Key Control wird in der Risiko-Kontroll-Matrix genau dokumentiert.
- Die Risikobewertung erfolgt durch eine realistische Einschätzung von Schadenshöhe und Eintrittswahrscheinlichkeit.
Die "Praxis Schulung IKS" erklärt die Anwendung der Key Controls im Detail.
The risk-control-matrix includes all key controls that have been identified and set up by the process managers for their processes. A key control is a financially risky control step whose risk is identified and assessed. The risk assessment and the traceability of the execution of the key control is precisely documented in the risk-control-matrix, which consists of several parts.
Process Information
- Process ID
- Process name
- Key Control ID
- Process manager
- Process step/activity
Check for ICS relevance
- Financial risk
- Key Control - yes or no
- Further procedure
Risk Assessment
- Risk owner
- Risk description
- Impact of the risk
- Risk assessment - amount of damage and occurrence
Control information
- Control description
- Control responsibility
- Control cycle
- Type of control
- Proof of control
Last evaluation
- Date
- Auditor
- Result of the sampling
In der Risiko-Kontroll-Matrix werden alle Key Controls aufgenommen, die in einer Erhebung durch die Prozessverant-wortlichen festgestellt wurden. Unter einer Key Control ist ein finanzrisikobehafteter Kontrollschritt zu verstehen, des-sen Risiko vom_von der Prozessverantwortlichen erkannt, bewertet und mit einer bestimmten Kontrolle versehen wird. Die Risikobewertung und die Nachvollziehbarkeit der Durchführung der Key Control wird in der Risiko-Kontroll-Matrix genau dokumentiert.
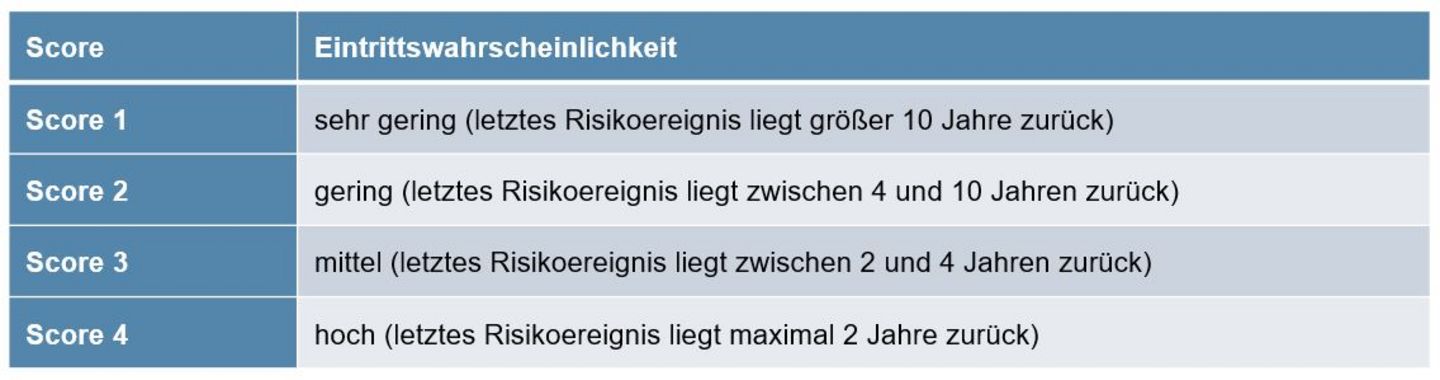
Eintrittswahrscheinlichkeit
Die Eintrittswahrscheinlichkeit wird in Jahren gemessen und zwar muss jener Zeitraum gewählt werden in dem der Risikoeintritt erwartet wird. Diese Bewertung ergibt sich aus einer realistischen Einschätzung bzw. auf Basis von Erfahrungen.
Score 1: sehr gering: > 10 Jahre
Score 2: gering: 4 – 10 Jahre
Score 3: mittel: 2 – 4 Jahre
Score 4: hoch: 0 – 2 Jahre
Schadenshöhe
Das Schadensausmaß wird mit Beträge von 0,3 Mio. bis 5 Mio Euro bewertet. Die Einschätzung des Schadensausmaßes beschränkt sich nicht nur auf den erwarteten Schaden für das eigene Strukturelemente, sondern für die gesamte TU Wien.
Score 1: unwesentlich < 0,3 Mio. pro Jahr
Keine spürbare Auswirkung auf Forschung oder Lehre
Score 2: minimal 0,3 - 1 Mio. pro Jahr
Kleinere Beeinträchtigungen der Lehre und kleinere Behinderungen der Forschung
Score 3: wesentlich 1 - 5 Mio. pro Jahr
Erhöhung des Dropouts und der Studiendauer sowie Verlust von Forschungskompetenz, -renommee (Drittmitteln)
Score 4: gefährdend > 5 Mio. pro Jahr
Beinahe Zusammenbruch der Lehre, überwiegende Einstellung der Forschung
Risikoberechnung
Der Gesamtscore für das Risiko ergibt sich durch das Aufsummieren der Scores z.B.:
"Score 1 sehr gering: > 10 Jahre" + "Score 1 unwesentlich < 0,2 Mio pro Jahr" = 2
Als kritische Risikobewertung wird ein Gesamtscore von 5 und größer gesehen. Diese Key Controls werden in den jährlichen Stichproben bevorzugt überprüft.
Die "Praxis Schulung IKS" erklärt die Anwendung der Risikoberechnung im Detail.
The probability of occurrence is measured in years. The time period in which the risk is expected to occur must be selected. This evaluation results due to realistic assessment or on experience.
The extent of the damage is estimated at between 0.3 million and 5 million euros. The assessment of the extent of damage is not limited to the expected damage for the own structural element (department, division), but for the entire TU Wien.

The total risk score is calculated by adding up the scores, e.g. "Score 1 very low: > 10 years" + "Score 1 insignificant < 0.2 million per year" = 2:
"Score 1 very low: > 10 years" + "Score 1 insignificant < 0.2 million per year" = 2
A total score of 5 and higher is considered a critical risk assessment. These key controls are prioritised in the annual random checks.
.
Further information is available to process managers at ICS Workplace, opens an external URL in a new window.
The annual update follows the ICS cycle:
- The ICS officer sends an email to the process group manager.
- Completeness of the process manager is checked.
- Process managers are informed about upcoming updates/reviews of necessary new processes/risk control matrix creation.
- Legal and compliance checks are performed as needed.
- 1. Approval of the updated/newly created processes including the risk control matrix by the process manager.
- 2. Approval by the ICS officer.
- 3. Approval by the process group manager.
- The entire risk control matrix is updated.
- Processes are updated on the website.
- Annual spot checks of key controls are conducted.
- Annual reporting to the Rectorate